Supercritical fluids are a fascinating state of matter that exist at temperatures and pressures beyond their critical point. This unique phase exhibits properties of both liquids and gases, creating intriguing possibilities for various applications.
In this blog post, we delve into the characteristics of supercritical fluids, highlighting their unusual behavior at the critical point. We will also explore some commonly used supercritical substances in industry.
Moreover, you’ll discover diverse applications where these remarkable fluids come into play – from pharmaceuticals to food processing. Lastly, we’ll discuss the benefits that make supercritical fluid technology an attractive option for those who would like to use it as an efficient extraction method.
What is Supercritical Fluid?
A supercritical fluid is a substance that has been heated and pressurized beyond its critical point, resulting in a state of matter that combines properties of both liquids and gases. This unique phase occurs when the temperature and pressure exceed the substance’s critical point, which varies for each material.
Don’t worry if this concept sounds complex – supercritical fluids are more common than you might think. They’re used in everything from food processing to waste management systems.
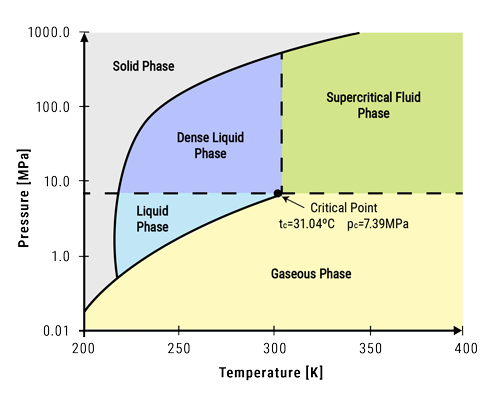
The Critical Point: A Brief Explanation
In thermodynamics, every pure compound has a specific temperature-pressure combination at which it can exist simultaneously as gas and liquid – this is known as the critical point. Beyond this threshold, distinguishing between these two states becomes impossible because they merge into one homogeneous phase – hence the term ‘supercritical.’
Supercritical Fluids: Bridging The Gap Between Liquids And Gases
In their supercritical state, fluids behave partly like gases (due to their low viscosity and high diffusivity) while also demonstrating some characteristics typical of liquids (like high density). This dual nature gives them an edge over traditional solvents since they can penetrate solid materials like gases yet dissolve compounds similar to liquids. As such, supercritical fluids have found widespread use across various industries, including food processing (via Supercritical Fluid Extraction) and pharmaceutical manufacturing (through Supercritical Anti-Solvent techniques).
An Everyday Example Of A Natural Supercritical Phenomenon:Geyser Activity: Did you know that geysers erupting hot water jets skywards is an example of naturally occurring supercritical behavior? When heated by magma-heated rocks deep within Earth’s crust, the underground water is transformed into superheated steam due to its immense pressure. However, the immense pressure at such depths prevents it from escaping upwards immediately, causing temperatures and pressures to rise well past its critical points and turning ordinary H2O into a supercritical version of itself.
Supercritical fluids are fascinating substances with unique properties that make them useful in a variety of applications. Who knew that something so complex could be so common?
Characteristics of Supercritical Fluids
Supercritical fluids possess unique characteristics that set them apart from liquids and gases, making them ideal for various industrial applications, particularly in botanical extraction.
Density
Supercritical fluids have a density higher than gases but lower than liquids, giving them excellent solvating power for efficient extraction processes.
Solvating Power
Supercritical fluids have high solvating power, allowing for precise and efficient extraction of specific compounds from plant material.
Diffusivity
These fluids exhibit behavior more similar to gases than liquids, with high diffusion coefficients that easily penetrate solid materials for effective extraction.
Compressibility
The compressibility factor allows for the manipulation of density and solvent strength by adjusting pressure conditions during extraction, enabling precise targeting and isolation of desired components.
Tunability
Adjusting parameters such as temperature and pressure allows for optimal states for different tasks, enhancing the flexibility and utility of supercritical fluids across diverse industries.
Overall, the unique characteristics of supercritical fluids make them powerful tools in modern industrial operations, especially where purity, efficiency, and environmental considerations are paramount.
Commonly Used Supercritical Fluids
A plethora of substances can be employed in their supercritical state for industrial purposes, making the world of supercritical fluids extensive and multifaceted. The most commonly used supercritical fluids are carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and other organic compounds.
Carbon Dioxide: A Popular Choice
Supercritical Carbon Dioxide (SC-CO2) has rapidly become the most popular option among all supercritical fluids, due to its advantageous properties that make it ideal for a wide range of applications. SC-CO2 is non-toxic, non-flammable, and readily available at a reasonable price, making it an attractive choice for use in food processing and pharmaceutical extraction processes. Its high solubility and low viscosity can be used in various ways to increase efficiency as well as ensure safety during handling. For example, supercritical CO2 can be used to extract desired substances from raw materials without the need for harsh chemicals or solvents; this process is also known as ‘supercritical fluid extraction’ (SFE). In addition, SC-CO2 is a versatile medium for cleaning components in food and beverage production, offering fast and effective dissolution of organic substances such as fats and proteins. Furthermore, its temperature stability makes it suitable for use with sensitive products that require precise control of temperature during extraction or purification processes. The combination of these unique features has allowed SC-CO2 to become a widely used tool across many industries.
The Role of Water: Beyond Hydration
Beyond its role as the universal solvent in our daily lives, supercritical water (SCW) plays a significant part in several industrial processes too. SCW is primarily utilized for waste treatment methods where high temperatures and pressures help break down complex molecules into simpler ones.
Ethanol & Other Organic Compounds: Versatile Players
In addition to CO2 and H2O, other organic compounds like ethanol have found utility as a supercritical fluid, especially within botanical extraction procedures. Ethanol’s polarity allows it to extract both polar and non-polar compounds effectively from plant material while maintaining safety standards given its generally recognized safe status by the FDA. Other common organic solvents include propane or butane, which, despite having lower critical points compared to CO2, are often preferred for specific extraction purposes due to their ability to dissolve certain types of materials more efficiently.
However, the use of ethanol and other organic solvents is not without risks due to their highly flammable nature in certain concentrations. As a result, safety protocols must be strictly enforced when using these compounds, such as exhaust fans to prevent buildup of fumes and proper ventilation to reduce the risk of fire. It is also important to monitor the temperature of the material during extraction, as some materials can ignite if exposed to elevated temperatures over a sustained period. Proper maintenance of equipment is essential to ensure it is functioning properly and to reduce any risks associated with improper extraction. The use of safety equipment such as gloves, goggles, and face masks is also strongly recommended. Additionally, proper storage and disposal of these chemicals must be followed to minimize potential environmental damage from their release into the environment.
Choosing the Right Supercritical Fluid
The selection of a particular fluid is contingent on the desired results from the process. Each substance offers different advantages based on factors such as cost, availability, environmental impact, safety considerations, and solvating power. Hence understanding these characteristics will enable you to make informed decisions about which fluid would best suit their needs. When it comes down to choosing between different options available – whether it’s carbon dioxide, water, or any other compound – every decision should be guided by careful consideration regarding desired outcome vs potential trade-offs involved.
Applications of Supercritical Fluids
Supercritical fluids have unique properties that make them useful in various industrial applications, particularly in extraction processes. Let’s explore some common uses.
Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE)
SFE is a popular application of supercritical fluids, widely used in industries such as pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals to extract specific compounds with precision and purity. This technique uses the solvating power of these substances to extract specific compounds from solid or liquid materials. SFE is commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals, where precision and purity are crucial.
Beverage Industry
In the beverage industry, supercritical carbon dioxide is often used for decaffeination processes. Its high diffusivity allows it to penetrate deep into coffee beans or tea leaves, selectively removing caffeine while leaving other flavor components intact – resulting in decaffeinated beverages with full flavor.
Cosmetics & Personal Care Products
The cosmetics industry also takes advantage of this technology for extracting essential oils without damaging delicate aromatic compounds that give each oil its characteristic scent profile – an aspect crucial for products like perfumes and scented lotions.
Environmental Applications
Supercritical fluids play a significant role in environmental remediation efforts due to their ability to dissolve non-polar contaminants found within soil or water sources. For instance, supercritical water oxidation (SCWO), which utilizes superheated water under pressure, has proven effective at breaking down organic pollutants into harmless byproducts.
Nutraceutical Industries
Nutraceutical industries extensively utilize SFE techniques due to their efficiency and selectivity characteristics, allowing them to isolate beneficial phytochemicals from botanical sources effectively – a key step towards creating potent dietary supplements.
Benefits of Using Supercritical Fluids
In the world of botanical extraction, supercritical fluids have become a game-changer due to their unique properties and benefits. These benefits not only include improved product quality but also increased efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and environmental friendliness.
Improved Product Quality
SFE allows for the selective extraction of desired components from raw materials, resulting in a pure and high-quality end product that meets industry standards. SFE selectively extracts desired components from raw materials while leaving behind unwanted substances. The outcome is a highly pure, superior quality end product that complies with industry criteria.
Increased Efficiency
Supercritical fluids penetrate solid matrices more efficiently than traditional solvents due to their high diffusivity property. This leads to faster extraction times and higher yields – crucial factors for businesses looking to increase productivity without compromising on quality.
Reduced Energy Consumption
Studies show that using supercritical fluids can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to conventional methods like steam distillation or solvent extraction. These fluids operate at moderate temperatures, requiring less heat input, which translates into lower energy costs – an attractive proposition for any entrepreneur concerned about sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Eco-Friendly Approach
Supercritical fluids are environmentally friendly since they reduce waste generation during the process. One commonly used supercritical fluid in industrial processes is CO2, which is recyclable. Its usage results in minimal emissions into the environment, making this method a green alternative compared to traditional techniques involving hazardous chemicals.
To sum up: if you’re an entrepreneur exploring options for botanical extractions or other applications where separation processes are involved – consider leveraging the power of ‘Supercritical Fluid’. It’s not just about staying ahead competitively by producing superior products but also contributing positively towards reducing our carbon footprint on Earth.
Conclusion
A supercritical fluid is a state of matter which has both gaseous and liquid characteristics, making it a hot topic in various industries.
Supercritical fluids are set apart from other states of matter, such as high solvating power and tunable properties.
Commonly used supercritical fluids include carbon dioxide, water, and ethanol, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
Using supercritical fluids in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and cosmetics manufacturing can offer several benefits, including increased efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Supercritical fluid extraction is a popular application of supercritical fluids, used to extract compounds from natural sources from plants.
Overall, the unique properties of supercritical fluids make them a valuable tool in various industries, with the potential for even more applications in the future.
Looking for high-performance supercritical CO2 extraction equipment? Look no further! ExtraktLAB is at the forefront of botanical extraction technologies, ranging from CO2 extraction to distillation and chromatography. Their cutting-edge advancement lies in the automated extraction to distillation process, a revolutionary technology that eliminates the requirement for ethanol and significantly reduces labor costs. If this piques your interest, feel free to reach out to our subject matter experts experts at 651.600.0036 or simply fill out our contact form. An expert will promptly get in touch with you to discuss your requirements.
Get in touch with our team to request a quote, learn more about our facility design services, or get help with your business plan.
We are dedicated to providing you with the best advice, quality, and service in the industry.



