Supercritical CO2 is a fascinating scientific method that converts carbon dioxide to a liquid state that makes it very efficient for extraction. This method has been used for a number of years to safely and efficiently extract a number of products from coffee to cooking extracts to CBD and botanical distillates. But, how exactly does carbon dioxide become supercritical, and how is that extraction method used successfully? In this post, we will discuss the basic composition of CO2, what it takes for CO2 to become supercritical, and how Supercritical CO2 is utilized in the extraction industry.
What is Carbon Dioxide (CO2)?
If you paid attention in your high school chemistry class, you might remember that CO2 is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature and regular pressures composed of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. You may also remember that most animals exhale carbon dioxide, or that plants take in carbon dioxide. Or, perhaps you may remember that CO2 is an important greenhouse gas that traps heat inside the Earth’s atmosphere. All of these things are true, and it is important to recognize that this gas is prevalent, relatively safe, and useful for a number of purposes.
For example, canisters filled with pressurized CO2 can be used to inflate bike tires and life jackets. CO2 is also used to carbonate soda, beer, champagne and other beverages. There are a prevalent number of practical uses for CO2 outside of the extraction industry in its gaseous, or even solid form, but it’s the liquid form of CO2 that is necessary for extraction, otherwise known as its supercritical state.
What Makes Supercritical CO2?
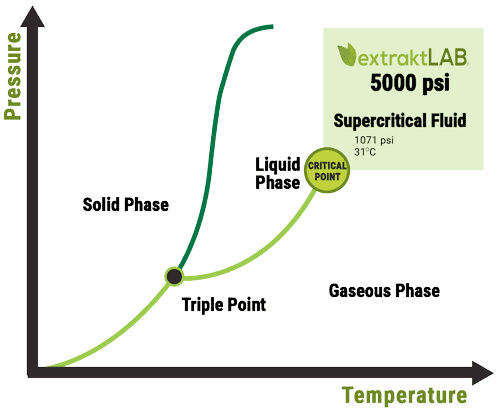
Because CO2 is not naturally a liquid in regular temperatures and pressures, it is not capable of being used as an extraction solvent without some alteration. In order to do this, pressure and temperature must be manipulated to very specific variables so that it reaches a liquid form. The graph below illustrates the specific variables for CO2 to reach its supercritical state:
As illustrated in the above graph, CO2 reaches its supercritical state at a pressure of 1071psi and 31 degrees celsius. Once this point has been reached, CO2 is no longer in its gaseous state and converts into a supercritical fluid. At this point, the supercritical CO2 acts similar to a liquid solvent such as ethanol. It is then capable of saturating the hemp biomass and stripping plant compounds from the material before being evaporated off and recycled for reuse.
What is Supercritical CO2 used for?
Now that we have explored supercritical CO2, where is it being used? The world of extraction is clearly not limited to the hemp industry. In fact, there are many industries that have utilized CO2 in their business well before it was ever used to extract hemp compounds:
Decaffeinated Coffee
Though many people enjoy a strong cup of coffee to start their day, plenty of others enjoy a cup without getting the jitters. Supercritical CO2 is often the extraction method used to remove the naturally occurring caffeine from the coffee beans. This is among the most prevalent uses of CO2 and is a much safer alternative to the solvents previously used for decaffeination including methylene chloride, ethyl acetate, trichloroethane and other potentially harmful solvents. Similar methods are also used to decaffeinate tea and other beverages.
Hops Extraction
Hop extracts can be used for brewing beer and supercritical CO2 is by far the safest method to obtain them. Because of its potency, these extracts are often used in high-hopped beers like IPAs. Once the resins are extracted from the hops plant material, it is packaged and distributed to brewers who are able to use it on an industrial scale.
Cooking Extracts
While other solvents like food grade ethanol are still popularly used in this type of product, cooking extracts like vanilla, maple, and others are often extracted using supercritical CO2. While other solvents are efficient in this field of extraction, there is little doubt that CO2 is the tried and true “clean and green” method for extracting consumable products like these.
Essential Oils
These products are sweeping the world market and are used for a variety of purposes including air fresheners, holistic remedies, cooking products and more. Similar to hemp extraction, essential oils are pulled from the plant material by saturation of fluid CO2 as a solvent. Once the plant oils have been stripped from the remaining plant material, the CO2 is evaporated off and recollected in the same process as CBD extraction.
The Supercritical CO2 Process of Extraction
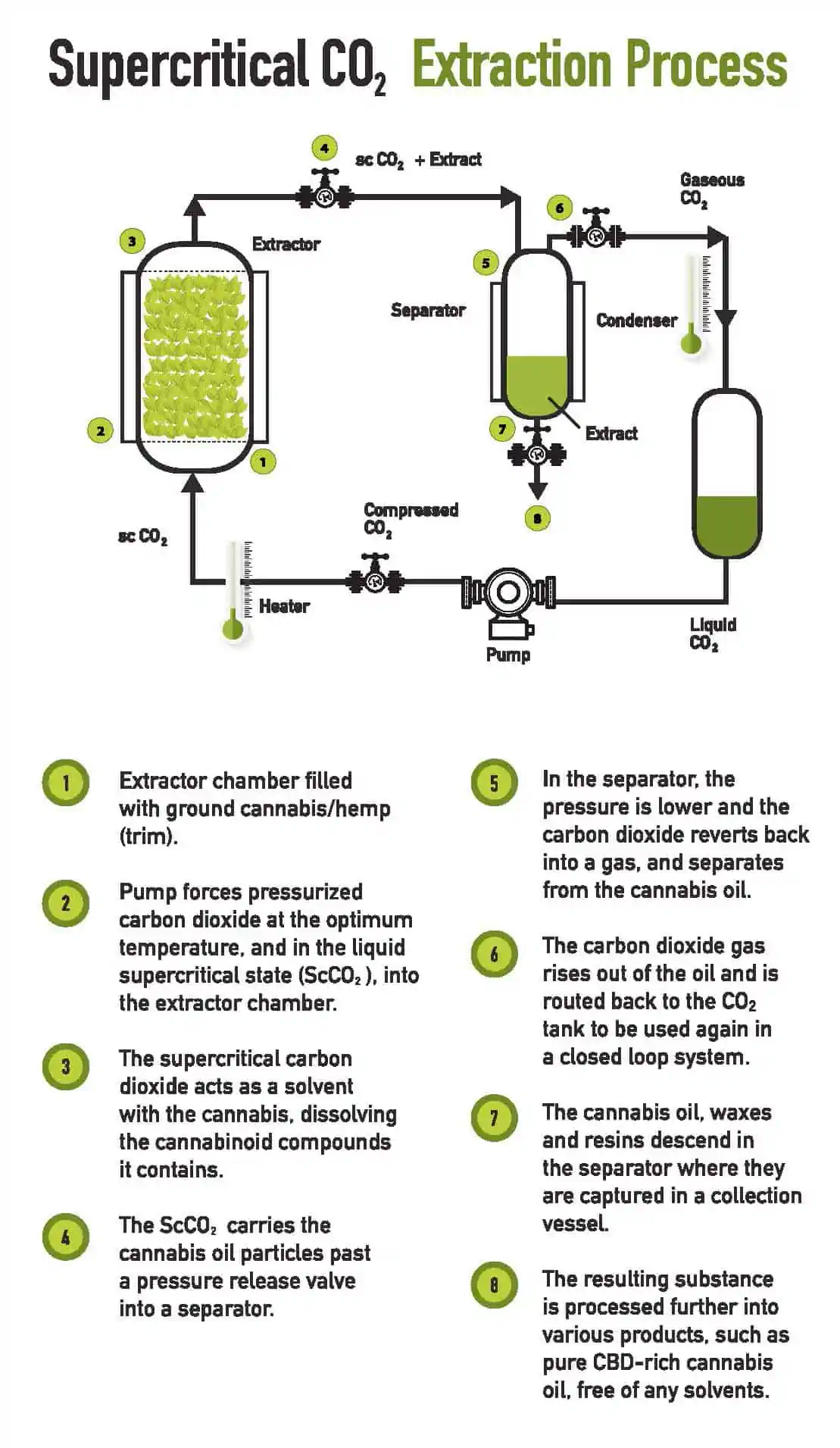
Many of the above mentioned products created from supercritical CO2 extraction are essentially made in the same way. For purpose of example, we will focus on hemp extraction and take a look inside the step by step process of CO2 extraction
Supercritical CO2 extractors use carbon dioxide (CO2) at an elevated temperature and pressure of 31ºC and 1071 psi which then becomes a supercritical fluid. In this state supercritical CO2 has an increased capacity for the diffusion of molecules and solubilizing non-polar compounds. Raising the temperature and pressure of the liquid CO2 even further provides highly efficient extractions of oils in a short period of time. Take a look below at the process step by step:
Why Supercritical CO2 is the Superior Extraction Method
We’ve covered the basics; what CO2 is, how it is used in its supercritical state and how SCCO2 extractors operate. Now, why is this extraction method the best option?
Clean and Green
CO2 extraction systems are often the cleanest extraction option overall. Because CO2 is considered a natural solvent, processors can more easily become a certified organic manufacturer and consumers can rest easy knowing that chemical residuals are a non-issue. CO2 also does not contribute to emissions into the environment when recycled properly making it the “clean and green” extraction option.
Processing Costs
CO2 extraction is a far less costly extraction method compared to other extraction solvents. For example, CO2 is 4 cents a pound compared to ethanol which can be roughly $4 per pound. Solvent losses also contribute to overall cost. As an example, 1-ton-per-day ethanol extraction systems would see an estimated $1,260,000 in solvent costs in just one year compared to just $42,048 using CO2.
Safest Products for Consumers
Because there are no chemical denaturants or volatile solvents left over in a CO2 extracted product, there is little doubt that it is the safest extraction process for consumers. A natural and organic solvent like CO2 means customer assurance without sacrificing product potency making CO2 extraction systems the best choice for unadulterated products that are certainly safe for regular consumption.

Final Thoughts
Supercritical CO2 has become the preferred method for extracting CBD oils to serve markets with the most demanding standards for safety, quality, purity and consistency. It is also preferred by consumers for the same reasons. For these reasons, extraktLAB chooses to utilize this preferred extraction method and advocate other hemp processors to do the same.