THC Remediation
Efficient Hemp Remediation with pure99
For a hemp extract to be legal under the 2018 Farm Bill, any particular hemp product must contain less than 0.3% tetrahydrocannbinol (THC), a psychoactive cannabinoid. In order to perform succesful THC remediation, chromatography becomes completely necessary and pure99 is the optimal solution for THC removal.
pure99 Chromatography System Enables THC Remediation At Scale
Farm Bill compliant hemp contains less than 0.3% THC, the compound that is responsible for psychoactive effects.
Lawmakers limited the amount of THC that could be present in hemp biomass so as to distinguish it from other plants that produce high amounts of the psychoactive component.
When the biomass is extracted, however, the amount of THC in the extract is at a higher level than the limit that was established by the Farm Bill. As the oil becomes more refined, the concentration of THC will increase to the point where the oil is no longer fit for commerce.
As a result, many producers have added a separation process into their hemp processing workflow. Hemp extract that has had THC removed from it is known as broad spectrum hemp oil. The production of broad-spectrum hemp oil typically requires the separation of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) from the other cannabinoids in the oil.

Where Does THC Remediation Fit In The Hemp Processing Workflow?
Typically, hemp biomass is extracted with supercritical CO2. This enables a clean and efficient way to produce high quality clinical grade hemp extracts.
The next step is to distill the hemp extract. Distillation will increase the potency of both CBD and THC and also remove a significant amount of the plant matrix, giving a clear distillate that is largely free from waxes and resins.
Typically, a producer will distill the hemp extract several times to improve the purity. We recommend that the producer distill the hemp extract twice before chromatography.
Once a hemp extract has been distilled, it is ready for chromatography. Hemp extract is typically dissolved in a solvent and injected onto a chromatography column. The separation takes place on the column and the equipment directs each component into a different vessel.
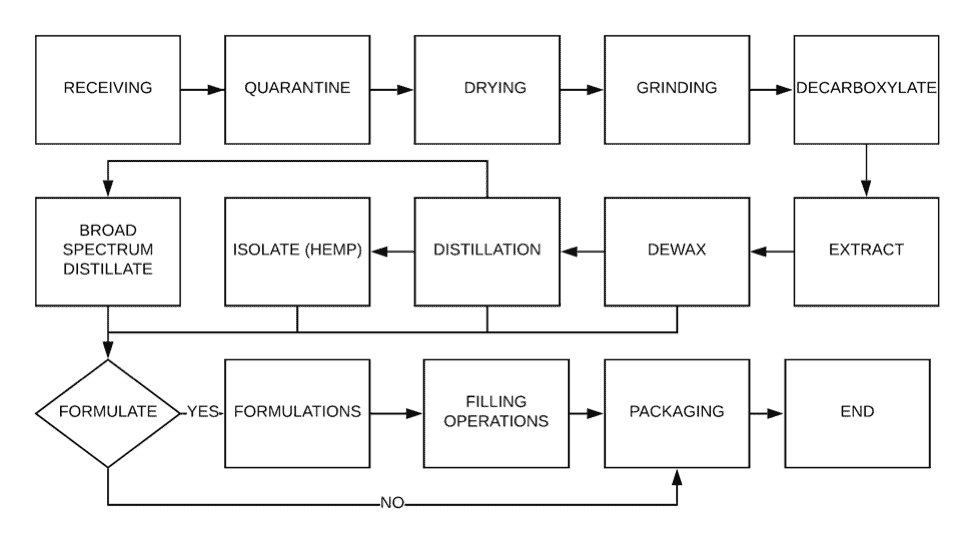
What is Broad Spectrum Hemp Extract?
Broad spectrum hemp extract is an oil that is derived from hemp but does not have any detectable THC in the material.
Many consumers desire broad spectrum hemp extract over isolate or crystal extract. This is due to the fact that the broad spectrum hemp carries with it not only CBD but also has the vital nutrients that remain in the extract after chromatography.
pure99 THC Remediation Machine
We have the perfect thc remediation machine for small, medium and large producers. Our CBD isolation machines produce multiple kg of broad spectrum distillate every hour.
THC Remediation Techniques
There are several different ways to remove THC from the hemp oil, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The following lists the primary methods:
• Chromatography (flash chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography)
• Degradation
• Liquid-Liquid Extraction (centrifugal partition chromatography)
• Crystallization
Crystallization
One of the most effective ways to remove THC is to simply crystallize out the CBD. This crystallization process typically will crystallize CBD and leave the matrix and THC giving a white isolate powder.
However, many consumers desire to maintain the plant characteristics including the phytonutrients that are discarded in the crystallization process, such as flavonoids, terpenes and carotenoids.
This consumer demand has given rise to several other different ways to remove THC from CBD while maintaining much of the integrity of the phytonutrients and plant components.
Degradation
One technique that effectively removes THC from oil is degradation of the THC into CBN by exposure to light and oxygen. However, this technique also degrades the oil into a black sludge that is highly undesirable for consumption. In addition, as the THC is being degraded, the target molecule CBD is also being degraded. So this technique is not very selective in the sense that it will target one compound over the other.
Liquid Liquid Extraction
Another technique is liquid liquid extraction. This involves exposing a sample to two separate solvents that are not miscible with each other.
A good example of a two solvent system is an oil-vinegar salad dressing. If you add herbs and spices into the two solvent dressing, shake, and let it separate, the flavors that are soluble in the oil phase will be found in the oil phase. Similarly, flavors that are more water soluble, will end up in the vinegar phase. This is liquid liquid extraction.
A form of liquid liquid extraction that involves a pumping mechanism is known as centrifugal partition chromatography. This technique exposes the sample to a cascade of two solvent system extraction operations and uses centrifugal force to move the products from extraction step to extraction step. Even though this technique can separate based on a series of liquid liquid extractions, it is more like liquid liquid extraction than chromatography because it does not have a stationary phase.
Counterflow current chromatography is another technique that uses immiscible liquids in a countercurrent flow to improve the exchange rate and efficiency of extraction.
All of these techniques require multiple passes with multiple extractions. Keep in mind to increase costs as the number of passes increases.
Chromatography
Another technique for hemp remediation is chromatography. This technique is widely used in pharmaceutical, food, and all kinds of manufacturing industries around the world. Due to its versatility and reliability, chromatography has enjoyed ubiquitous adoption for separations of complex mixtures.
Chromatography is a separations technique that uses stationary phase (particles) to separate a mixture into its pure components. This is accomplished by:
Step 1. Dissolving the mixture to be separated into a suitable solvent known as the mobile phase. A high pressure pump usually provides the solvent flow through the packed bed.
Step 2. Introducing that mixture into the flowing stream with an injector.
Step 3. The individual components of the mixture then encounter a column packed with stationary phase particles. The components interact with the stationary phase differently, some stronger than others. Weakly interacting components move across the column faster than those components that interact strongly. Thus, the components will migrate along the column at different rates.
Step 4. Each component exiting the column encounters a detector that will indicate that a compound is ready to be collected.
Step 5. A valve is actuated to give the component a vessel to occupy.
Step 6. The process repeats when the detector senses a different compound coming out of the column, except a different valve is actuated and the second component is collected in a completely different vessel than the first component.
Pros and Cons of THC Remediation Methods and Techniques
The table below compares and contrasts the different pros and cons for each remediation technique.
| Recovery | Selectivity | Throughput | Cost / Gram | |
| Chromatography | HIGH | HIGH | HIGH | MED |
| Degradation | LOW | LOW | HIGH | HIGH |
| Liquid-Liquid | LOW | LOW | HIGH | HIGH |
| Crystallization | MED | HIGH | HIGH | MED |
Cost per Gram for THC Remediation
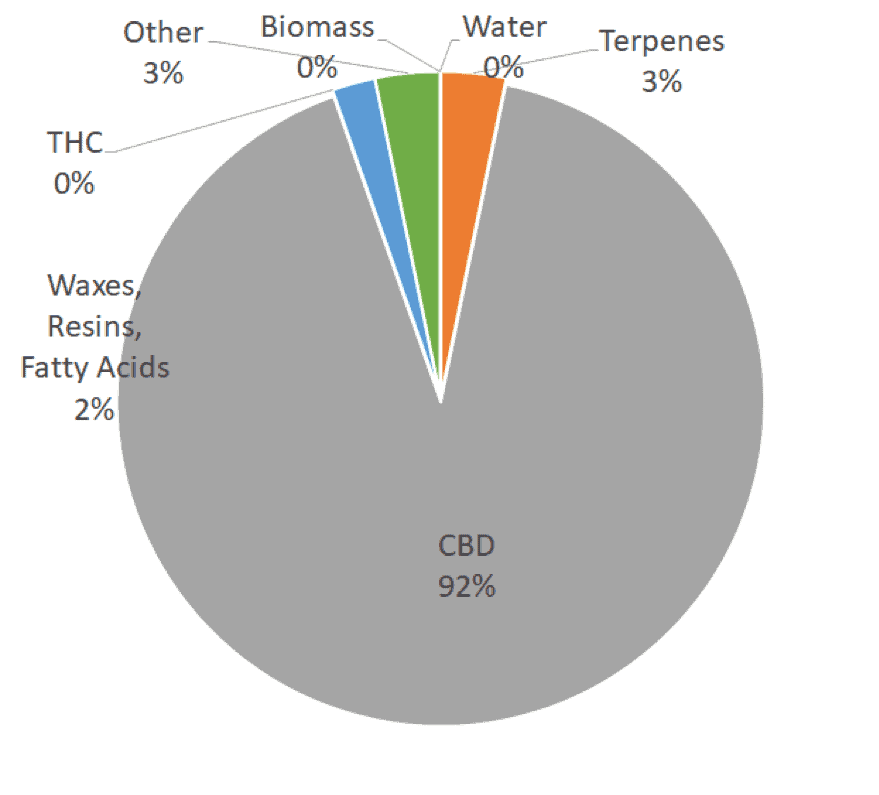
The cost of loss of hemp extract at the THC remediation stage is very costly. It is important to weigh the solvent cost, the operating costs, the recovery cost with the cost of capital equipment in order to make a wise judgment.
The number one cost contributor to each technique’s overall cost per gram is the RECOVERY OF CBD during the process.
Due to low recovery of high cost input materials (distillate or isolate or crude), degradation, liquid liquid such as centrifugal partition chromatography (CPC) and counter current chromatography are high cost per gram.
Due to chromatography’s high recovery, the cost per gram is low and outweighs the cost of stationary phase recycling. Stationary phase recycling can be costly if a proprietary stationary phase is used.
Throughput
Chromatography can be scaled to address high-throughput requirements but the capital costs of doing that are greater compared to compared to liquid-liquid extraction, degradation and crystallization. However, this is not the case with centrifugal partition chromatography or counter flow current chromatography; these techniques have a high capital cost to scale up.
Liquid extraction and crystallization methods have the advantages of high throughput. However, liquid techniques have much lower selectivity compared to chromatography and therefore the recovery suffers.
Recovery
Degradation of all THC into CBN using light and heat is not a viable technique for removal of THC from CBD or hemp extract. The main reason for that is the recovery is very low and the extract itself is highly degraded. However, degradation techniques are typically very low cost. Chromatography by far has the highest recovery rate among the techniques.
Selectivity
Chromatography has tunable selectivity as defined by the method. This includes the stationary phase and the mobile phase. Methods can be changed to change the selectivity. This is also the case for liquid liquid techniques.
The key advantage that pure99 CBD chromatography has over the other techniques is that the selectivity is achieved with NO WATER in the eluent.
Separation Efficiency
The key advantage that chromatography has over centrifugal partition chromatography and countercurrent chromatography is efficiency. A typical high pressure chromatography process can generate thousands of separation plates per minute while typical CPC and CCC generate 10s to 100s of plates per minute.
Chromatography is the Best THC Remediation Method
There are many different THC remediation techniques. While there are other viable techniques, chromatography provides the best THC remediation method simply due to its high recovery, high throughput, high selectivity, and widespread application in separations processes.
Read our CBD Isolation guide process for producers.
Calculate Your Business Operating Cost
Starting an extraction Business? Check out our Calculators and to analyse costs, estimated revenue, yield, initial investments and important metrics for your extraction business.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I separate minor cannabinoids from major cannabinoids using the Pure99 Chromatography System?
We provide methods with the Pure99 system for THC and CBD separation. We also produce selective materials for CBN separation from THC/CBD. For other minor cannabinoids, the separation depends on how it will elute from the column in relation to the other major cannabinoids in the sample. That elution time and order depends on the column separation material known as the stationary phase, and the eluent, also known as the mobile phase. Scientists who are experts at finding unique conditions that will meet the goals of the separation are called chromatographers and they do methods development to find a suitable method.
What is the throughput of the Pure99?
Chromatography throughput for the specific example of the remediation of 1-3% THC in concentrated CBD can range from 1 kg to 6 kg per hour. Similar to distillation where the throughput will depend on the purity of the sample and how aggressive the cut is made, the throughput of a chromatography system is a trade off between purity of the final product and how aggressive the “cut” is made. It really depends on you. The general rule of thumb is that the sample will be more pure as the throughput decreases.
Do you provide SOPs for the Chromatography equipment?
Yes. We provide Standard operating procedures for analytical hplc, preparative hplc, GC headspace, and for sample preparation. We also provide start up kits for each one of these pieces of equipment along with sample management software called the igwLAB
Are the Chromatography Methods Validated for Cannabinoid Separation?
The customer validates the methods according to their company’s validation protocol. Chromatography and cleaning validation protocol for analytical methods are significantly different than production validation protocol and also very significantly from customer to customer.
Do Methods Come with the Pure99?
Yes. We provide the methods for separation of THC and CBD. If the customer desires to separate out other cannabinoids, they are welcome to develop their own methods.
What other Equipment is Required for the Pure99 to Function?
Other equipment and infrastructure besides the Pure99 is required to enable the proper functioning of a separations facility. These items include equipment that is either to measure how the method is doing overtime, equipment that is needed to measure how
HPLC with methods
fracTRON to remove solvents
Headspace GC with methods
Chillers and Heaters
Stainless or Glass Mixing Tanks
Drain Droid filtration
C1D2 Compliant Room
Solvent Storage Control Area
Is Cannabinoid Separation and Chromatography Training Included?
All of our chromatography products come with 2 days of training with optional on-site training at our demo facility in Osceola Wisconsin. Cannabinoid separation methods are also provided. Additional training for HPLC and for headspace GC is typically conducted at our facility in Osceola Wisconsin. On-site training for these items may be purchased by the customer.
Does distillation replace chromatography?
Chromatography and distillation are not analogous. Chromatography utilizes differences in chemical affinity to separate a mixture of components, distillation utilizes differences in boiling points. Wiped film distillation does not separate THC and CBD despite their differences in boiling points. Chromatography will separate THC and CBD into their pure fractions.
How do you remediate psychoactive cannabinoids from CBD oils?
There are several processes for the removal of psychoactive cannabinoids from CBD distillate. These include
1. Precipitation of CBD in a solvent
2. Chromatography separations.
3. Partitioning of cannabinoids in different organic solvents.
4. Degradation of psychoactive cannabinoids with oxidation and light.
In the isolate process, the CBD is precipitated from the oil in a nonpolar solvent blend Leaving the psychoactive cannabinoid in the supernatant to be discarded.
The second process is chromatography. In chromatography, cannabinoids are separated again in a solvent while flowing A packed bed of particles. This process can be frustrating for the end-user because it requires a high level of skill to conduct the separation. Oftentimes the particles can fail and plug up if the sample that is being separated has not been properly prepared. If done correctly, this process has the potential to separate out large amounts of CBD from psychoactive cannabinoids.
The third process involves separation by partitioning between two immiscible solvents. This process is very solvent intensive and is costly from the standpoint of solvent usage. There are also issues with solvent contamination of the final broad spectrum CBD oil. If done correctly, this process has the potential to separate out large amounts of CBD from psychoactive cannabinoids.
Finally, the last process involves degrading the Delta 9 into CBN with oxidation and uv light. The problem with this approach is that the CBD also degrades so the yield for this process is typically less than desirable.






