How to Make Cannabis Oil
Table of Contents
- How to Make Cannabis Oil From Trim
- CALCULATE Yield from Outdoor Hemp Grow
- Establish Your Trim Quality
- Four Grades of Trim
- Sampling Trim for Extract Oil
- Measuring for Potency, Indentity, and Pesticides
- How to Extract Cannabinoid Oils from Fresh Trim
- Extracting THC from Trim
- Refinement: Filtration, Solvent Removal, and Distillation
- extraktLAB has the Solution You Need
- FAQ
- Contact Us
How to Make Cannabis Oil from Trim
Learn the steps to extracting cannabinoid oil from trim whether you are a large scale grower, or a small scale operation, it is likely that you may have accumulated a quantity of trim that you don’t know what to with. The good news is that, with a little time and effort, you can create high quality cannabinoid extracts from your leftover trim in just a few easy steps. This article details the step by step process of how to make cannabis oil from trim and how the best practices you can follow to properly create high quality extracts.
Establish Your Trim Quality
Trim refers to the trichome-rich outer leaves that encompass the cannabis flower (or “bud”). The overall cannabinoid content of these leaves can range from 10-15%, and high-grade trim usually includes small flowers that cannot be sold elsewhere.
Even though many medical purveyors in oils-only states use both flower and trim as a source for the extract oils, some extractors use trim exclusively as the source material for their extractions.
Whether learning how to extract CBD, or how to extract THC from trimmings, hemp and cannabis trim can be obtained from a variety of producers, which means that the range of quality will also vary greatly.
The Four Grades of Cannabis Trim
Trim is generally classified into four grades based on a standard set of criteria, such as resin, trichome density, and several other factors used to determine its quality:
Grade 1 Trim for Extract Oil
- Resin Content: 15%
- Cannabinoid content: High
- Trichomes: High density
- Stems: None
- Fan Leaf: None
- Debris: Free from foreign debris
Grade 2 Trim for Extract Oil
- Resin content: 10-12%
- Cannabinoid content: High
- Trichomes: Medium density
- Stems: None
- Fan Leaf: None
- Debris: Free from foreign debris
Grade 3 Trim for Extract Oil
- Resin Content: 5-10%
- Cannabinoid content: low
- Trichomes: Low density
- Stems: None
- Fan Leaf: None
- Debris: Free from foreign debris
Grade 4 Trim for Extract Oil
- Resin content: 1-5%
- Cannabinoid content: low
- Trichomes: Low to no density
- Stems: Yes
- Fan Leaf: Yes
- Debris: Typically will have refuse
Sampling Trim for Extract Oil
Sampling is an important part of the grading exercise. For example, when a truckload of trim is purchased, Grade 1 and 2 are presented to the seller who typically makes the decision on whether the trim is “good” or “poor” quality by rubbing the material on his fingers to gauge the resin content. This method of determining good vs. poor is not objective and is very prone to mis-grading.

Measuring for Potency, Identity, and Pesticides
strong>Many extractors believe the only time an extract needs to be measured is when the product is shipped or maybe not even at all. A more refined approach includes measuring pesticides, potency, concentration, and identity before the trim is purchased.
This is accomplished with modern-day techniques using high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet (HPLC-UV), mass spectrometry (MS), and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The finger method is a good first approximation, but it can lead to erroneous results, even with an experienced buyer.
For example, some cultivars have a much higher resin content than others. And it is known that cannabinoid content varies with variety. Thus, you could be purchasing a high wax content material that would “finger test” well but have very low cannabinoid content.
How to Extract Cannabinoid Oil From Fresh Trim
There are several different methods you can use to extract hash oil from cannabis trim. Each method varies in its simplicity, scalability, and purity of output. Some of the most common extraction methods include:
- Butane extraction
- Ethanol extraction
- Supercritical CO2 extraction
Butane Extraction
One popular method on how to make cannabinoid oil from trim is by using a hydrocarbon solvent such as butane. Butane is nonpolar, so it is useful for extracting terpenes and cannabinoids from solution without unwanted plant material such as chlorophyll.
To avoid impurities, only high-quality commercial butane must be used for extraction. It is also necessary to purge the extract before consumption to ensure that all residual solvent has been removed. A major downfall of butane is that it is highly combustible; even a minor mistake during the extraction process could prove disastrous.
Ethanol Extraction
Ethanol extraction is another common botanical extraction method to consider for your cannabis trim. Ethanol is designated GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) by the US Food and Drug Administration, and it is highly effective at separating cannabinoids and terpenes from plant material. Like butane, though, ethanol is highly flammable – so great care must be taken when extracting cannabis oil with this method.
Ethanol is a polar solvent, so it also extracts unwanted plant material such as chlorophyll, waxes, and fats. When you want to remove the plant waxes and lipids from solution, winterization is a critical step in the process. Our popular DrainDroyd system provides a fast, simple solution for your extract filtration needs. The DrainDroyd allows you to filter and dewax up to five liters of cannabis oil in only five minutes. You can also read our post about how to remove dark colors from your extracts to learn more.
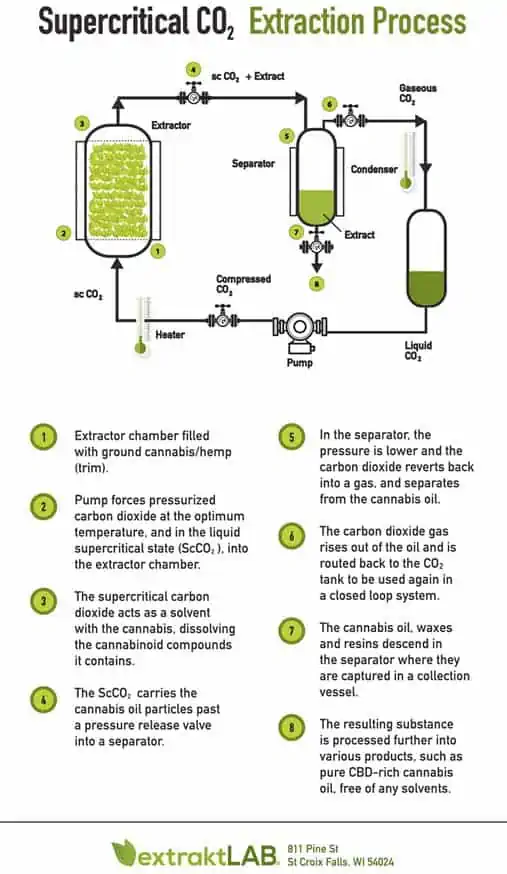
Supercritical CO2 Extraction
Using a supercritical CO2 extractor is the safest way to extract high-quality cannabis oil from trim at scale. CO2 extraction removes the high risk of flammability introduced by methods using volatile organic compounds such as ethanol.
The process of how to make THC oil, or CBD oil from cannabis biomass involves pressurizing CO2 until it turns into a liquid which is pumped through your plant matter. To separate the extracted compounds, the CO2 is converted back into a gas, leaving only the desired material behind.
Extracting THC from Trim
Though the majority of major cannabinoids are found in the flower or “bud” of the hemp or cannabis plant, with a little bit of hard work, extracting THC from cannabis trim is possible. With any of the above listed extraction methods, extracting THC is possible when done correctly.
As mentioned, the primary issue with extracting THC from trim is the quantity of trim available to the producer. Because the percentage of THC and other cannabinoids is exponentially more in the flower of the cannabis plant, it takes a very large quantity of trim to produce any kind of profitable yield when extracting THC.
The ideal choice for extracting THC is the use of cannabis or marijuana as opposed to industrial hemp. Where legal, cannabis is grown with the intentional cultivation of high levels of THC. This results in not only flower with high THC content, but trim that is “perfect” for extracting THC. Again, this will take a large amount of trim to perform, but trim produced from cannabis plants that yield higher percentages of THC are much more effective in creating THC extracts than trim produced from industrial hemp.
Refinement: Filtration, Solvent Removal & Distillation
No matter the method of extraction used, further refinement of the extracted product from your hemp or cannabis is necessary to create a safe, quality product. This is accomplished initially by filtration, solvent removal and by further distillation if possible, or necessary, depending on the scale and method of operation.
Filtration
No matter the scale of extraction, filtration is necessary to remove as much of the excess plant material as possible that is co-extracted with the desired cannabinoid oil. In a small scale, or at-home extraction, this can be as simple as straining the ethanol and extraction mixture through a sieve that will catch some of the fats, waxes and other unwanted plant materials.
In a large scale extraction operation, filtration is a much more refined process that tends to remove higher levels of plant materials along with other materials that are not so easily removed like chlorophylls that can cause a dark color and less desirable taste.
Filtration on this scale is often performed with a vacuum filtration apparatus coupled with a filtration media like activated carbon. This operation takes the solvent/extract mixture and pulls it through the filter media via the vacuum filtration apparatus. This effectively removes the majority of fats, waxes and chlorophyll from the cannabinoid oil that would otherwise add an unpleasant flavor and overall harsh experience to the end product formulated by the extract. With ethanol and butane, this is the next necessary step.
However, CO2 extraction requires a winterization process as well. This combines the extract with a small amount of food grade ethanol at very low temperatures. This helps to solidify the plant waxes and fats before being introduced to the filtration process to more effectively remove the undesirable plant materials from the extracted cannabinoid oil
Solvent Removal
In a smaller scale extraction operation, solvent removal is relatively straight forward. By applying heat to the extracted oil, solvents like butane and ethanol will begin to evaporate on their own. A very simple method for even at-home extraction is applying heat to a collection vessel with hot water. Similar to a double boiler for cooking, hot water can be added to a separate vessel with the vessel used to collect your oil resting inside of it.
Because ethanol and butane are volatile at higher temperatures, the increased heat from the hot water vessel will allow some of the solvent to evaporate from the cannabis or hemp oil extract. On a small scale, this may be the final step that will yield a relatively potent, quality product for personal consumption.
On a larger scale, specialized solvent removal equipment may be used for a more efficient process for higher extraction yields and increased quality. Supercritical CO2 extraction, for example, is very unlikely to be performed at a smaller scale due to the equipment necessary to perform the extraction process. By default, this makes larger scale solvent removal and distillation equipment essential. This equipment often incorporates rotary evaporators or falling film evaporators.
Though the basic principle of heat application remains the same, thin film technology coupled with vacuum pressure increases the effectiveness of the solvent removal process. Using a rotating flask or vertical columns, the oil is spread across the surface of the evaporator making it easier to volatilize the solvent in the mixture. The vacuum pressure allows for the necessary temperature to volatilize those solvents even lower, increasing the effectiveness of the solvent removal process and preventing cannabinoid and terpene degradation from higher temperature application.
Distillation
The intended goal is to get your extracts as close to 100% purity as possible. Filtration and solvent removal, while necessary, do not remove all of the impurities that come from the extraction process. The final distillation process allows for a cannabis or hemp oil extract that is as close to 100% purity as possible by removing the minute levels of solvents, terpenes, and other impurities.
In essence, the process is the same as solvent removal. Vacuum pressure, coupled with thin film and heat application helps to remove volatile solvents and other compounds. The difference in the final distillation process is the increase of viscosity as the extract is further refined. This is why equipment like a wiped film evaporator is used.
Again, the distillation process remains the same, but to combat that high viscosity, a wiped film uses a wiper blade to spread thin the distillate on the column of the evaporator so that the volatilization process can be increasingly effective. Doing this in a large-scale operation can result in potency levels near 100% whether that extraction method is ethanol, CO2 or hydrocarbons like butane.
In a smaller scale extraction operation, this final distillation process may not be entirely feasible. Because the solvent removal process is technically a distillation process, it may not be necessary (or possible) to perform proper distillation with a lack of equipment like a wiped film evaporator.
That said, creating a safe, potent extract on a smaller scale without higher tech distillation equipment can still be accomplished on a scale of personal use and should be relatively effective after the mentioned solvent removal process.
extraktLAB has the solution and knows how to make cannabis oil from trim
extraktLAB specializes in CO2 extraction equipment. Our high throughput supercritical CO2 extraction machines can produce 600 to 1,200 grams of extract per hour. We offer a variety of options suited to fit your desired level of output. You can view more information by visiting our Supercritical CO2 Extractors page which we have detailed guide about hemp processing, hemp extraction, extraction method and CO2 extraction process.
For more information about any of our products give our sales team a call at 651-600-0036.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you make CBD oil from leaves?
Although the vast majority of cannabinoids, including CBD, are located in the hemp plant’s flowers or buds, there may be 1% – 5% content within the leaves. Although the use of hemp extraction equipment is possible, the most efficient method would be infusion. Infusion is achieved by adding the plant leaves into a pot or vessel of oil (MCT, coconut oil, grapeseed oil, etc), apply medium heat for 4 four hours then strain out the plant material. The remaining oil will now contain CBD.
How do you make CBD isolate at home?
CBD isolation is the process required to make CBD isolate. This process includes the use of ethanol, butane, or CO2. Once the hemp biomass is in the extraction column it will combine with the desired solvent. After some time, it separates terpenes, fats, and waxes and provides the purest form of CBD.
The process of creating CBD Isolate requires pure, organic solvents and the ability to safely remove/recover said solvents. CBD Oil is blended with an organic solvent, then the mixture’s temperature is slowly reduced to cryogenic temperatures, forcing the CBD isolate/separate and create a crystalline like substance.
How do you extract THC from trim?
Plant cannabinoid content is determined by the variety or strain chosen. Some strains are designed to create high CBD content and some are designed to create high THC content. THC can be extracted with the same methods used to extract CBD: Supercritical CO2, Butane/Propane, Ethanol and water.
How to extract cannabinoid oil from fresh trim?
The best practice to extract cannabinoid oil from fresh trim is by supercritical CO2 extraction. There are other extraction methods, such as butane/propane extraction and, ethanol extraction. Each method varies in simplicity, scalability, and purity. Supercritical CO2 extraction is the safest, cleanest, lowest operations cost, and most environmentally sustainable method of extraction.
How much CBD is in hemp?
Cannabinoids, like CBD, are stored in the small resin glands on the surface of the hemp flower, these are called trichomes. Trichomes are mainly found on the flower or bud of the hemp plant and very rarely on the leaves. Current genetics allow for hemp flowers to contain 10%-25% CBD content.
Is hemp oil the same as CBD oil?
No. CBD oil is extracted from the flowers and leaves of the hemp plant and features a high amount of CBD. On the other hand, hemp oil is extracted from hemp seeds and does not contain CBD.
How do you extract CBD from stems?
Note: This process is something a DIY person might do, but a larger company wouldn’t do this as it would be a waste of time and money.
Although the vast majority of cannabinoids, including CBD, are located in the hemp plant’s flowers or buds, there may be 1% – 3% content within the stem/stalk. Although the use of hemp extraction equipment is possible, the most efficient method would be infusion. Infusion is achieved by adding the plant stems into a pot or vessel of oil (MCT, coconut oil, grapeseed oil, etc.), apply medium heat for 4 four hours then strain out the plant material. The remaining oil will now contain CBD.
What part of the plant is used for CBD oil?
Cannabinoids, like CBD, are stored in the small resin glands on the surface of the hemp flower, these are called trichomes. Trichomes are located predominantly on the hemp flower or bud, with minimal trichomes and CBD located on the leaves and/or stems. Typically, hemp extraction equipment is used to extract CBD from the hemp flowers and buds; Flower and bud trimmings are also used.