Cannabis Extraction
The cannabis industry has only increased in the last decade with legalization both medicinal and recreational, spreading across the country. However, things have changed since the days of smokable flowers and edibles. Today, cannabis extraction* is at the forefront of innovative, popular and profitable products in the industry. Because of this, producers need to realize the promise of cannabis extraction and learn how to perform this crucial process perfectly.
This article will discuss the very beginnings of cannabis extraction, cannabis extraction method, how the process is performed, the products it creates and more. This process is likely the most vital role in a cannabis producer’s repertoire to create or improve their business in a rapidly growing industry.
Cannabis Extraction Equipment
In this article, we explain cannabis extraction in detail – including cannabis extraction equipment from grinding to isolation and every step in between.
THC Extraction
With THC extract products ranging in potency from 75%-99%, practicing THC extraction methods are important for creating popular products that customers will seek out in the current market.
Introduction to Cannabis Extraction
Cannabis has been used for thousands of years, and while it has become more popular recently, various extracts have been used for the same amount of time. Though the various extracts will be explained later in this article, it is important to remember that, although cannabis extraction is finding new methods, its general principle remains relatively unchanged.
Perhaps the most unique change to cannabis extraction is the use of solvents to create brand new kinds of extracts like BHO, wax and shatter (more on those later). These extracts are a far cry from traditional extracts like hashish, kief, oils and butters. Without recent technology, these extracts were prevalent and created with simple methods. Because of the use of cutting edge extraction, filtration and distillation technology, cannabis extracts are incredibly potent and highly desirable by the medical and recreational industries. This means a very great opportunity has opened for producers all across the country.
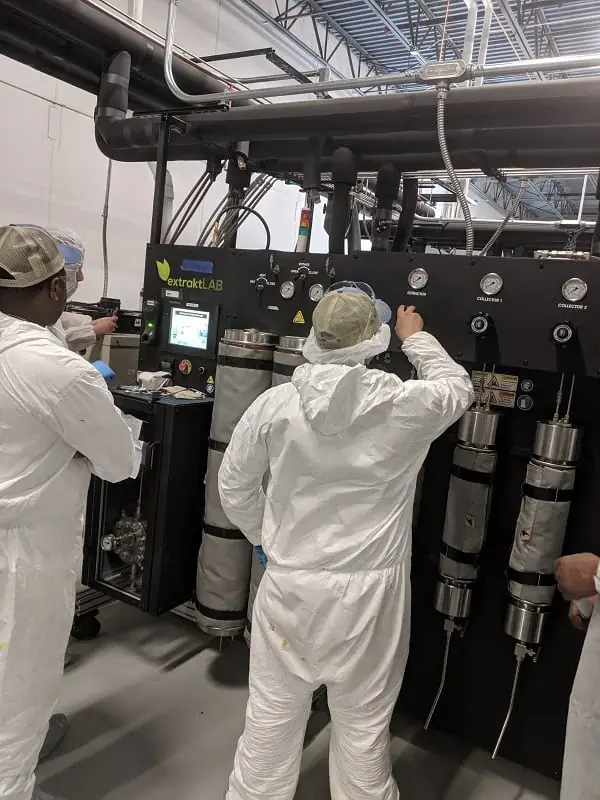

Cannabis Extraction Methods
While classic extracts like hash are still widely used, these new extracts are becoming exponentially more valuable indicating a need for a new cannabis extraction method. Among these various methods, solvent extraction is very popular due to its overall efficiency in producing quality extracts at a relatively high throughput. That being said, there are a number of solvents.
Solvents Used to Make Cannabis Extracts
Though there are a number of solvents used for cannabis extraction, not every cannabis extraction method is the same. There are some solvents that are more powerful, others more health conscious, and others still that are both. Let’s break down three of the most common cannabis extraction solvents in detail:
Hydrocarbon Extraction
Hydrocarbon solvents are effective, but not entirely safe for producers or consumers. It is vital to remember that common solvents in this category are hexane, propane and butane – all of which are very volatile. This poses an increased risk for fire and explosions. With that comes increased costs for blast-ready rooms, infrared gas detectors and C1D1 specifications that add to overall operational costs.
While the majority of these hydrocarbons are taken out of an extract during solvent removal, it is not guaranteed that the entirety of these byproducts will be removed. This means that consumers are faced with the choice of consuming a hemp or cannabis extract containing parts-per-million (PPM) of these solvents. There is little research to assume that continued, daily use of these products will have no long-term health effects over the course of a consumer’s life.
Ethanol Extraction
Ethanol is a very effective cannabis extraction method for extracting cannabinoids from hemp and cannabis. The problem, however, comes in the most common form used for extraction: denatured ethanol. Where food grade ethanol is a very safe option (think grain alcohol as an example) it is far too costly for any sustainable business model. Therefore, manufacturers turn to denatured ethanol which is Generally Regarded As Safe (GRAS) by the FDA, but contains chemical denaturants used to deter recreational consumption so that it can be sold as fuel, cleaners and other products without paying beverage taxes.
Although denatured ethanol is created with the intent of preventing human consumption, it is the common form of ethanol used in cannabis extraction. Like hydrocarbon extraction, solvent removal eliminates a significant amount of the ethanol left over from the extraction process, but it is never guaranteed that all of the ethanol is removed. In fact, the FDA allows for certain PPM of pentane, methanol, hexane and other denaturants in extracts that are still considered “safe” for consumption. It is unknown whether or not daily consumption of residuals could have lasting negative effects on the body.
Supercritical CO2 Extraction
Incredibly efficient in its supercritical state, CO2 is a fast, clean, low-cost extraction that is tried and true. For producers, CO2 can be used for drastically lower costs than ethanol or hydrocarbon extraction simultaneously eliminating costs for blast ready facilities due to lack of flammability. Because it is natural, it also allows for obtaining organic certification and reduces harmful emissions that are harmful to the environment.
In summary, CO2 extraction, ethanol extraction and hydrocarbon extraction can produce desirable CBD extracts; however, CO2 extraction has an edge over ethanol and hydrocarbon extraction due to clean, high throughput efficiency and the avoidance of risk related to chemical contaminants. CO2 extraction is also much less expensive than other extraction solvents. For those reasons CO2 is a better extraction process.

Types of Cannabis Extracts & Concentrates
- Butane Hash Oil (BHO): Created specifically from butane as its solvent, BHO can come in a variety of consistencies including wax, oil, crumble and others and is an incredibly potent extract that is typically vaporized for inhalation.
- Budder: This extract is often made through solvent extraction and is very sticky and gooey. That isn’t to say that this form of cannabis extract isn’t very potent – twice to three times that of cannabis flower on its own.
- Shatter: Created using solvent extraction, shatter is a transparent, glassy substance that earns its name from the brittle nature of its composition. This extract is often very potent ranging anywhere from 70-95% potency.
- Crumble: Often referred to as honeycomb, this extract is made through a variety of solvents and is roughly as potent as shatter. The difference in consistency is due to the presence of oxygen trapped in the extract similar to meringue made from egg whites.
- Rick Simpson Oil: Commonly referred to as RSO, this extract is commonly made at home using powerful food grade ethanol such as everclear to soak the entirety of the cannabis flower to create a dark, potent oil intended for ingestion. It is now a common extract used for medicinal purposes in very painful or debilitating diseases.
- Kief: Perhaps the most simple of extracts, “kief” is the result of trichomes that are sifted through a mesh screen – often in the bottom of a marijuna grinder. This powdery substance is relatively potent compared to the flower of the plant, but is not quite as potent as other extracts.
- Hash: similar to kief, hash or hashish has been used for many years all around the world. It is created in roughly the same manner, but often on a larger scale. The sifted material is then heated and pressed to make a solid brick that can be smoked whole or broken up and added to flower.
- Rosin: Gaining in popularity, rosin is created without a solvent, but yields very similar results to that of shatter. A heated press is used to crush the cannabis buds to create a slightly sticky, translucent extract without changing the chemical composition as solvent extractions do.
UPGRADE YOUR INDUSTRIAL HEMP MACHINE
Ask our industrial hemp experts to determine what type of hemp processing and hemp extraction equipment is best suited for your business.
Uses and Products from Cannabis Extracts
So, we’ve established many of the extracts are made through cannabis extraction, but how are they used? Because of their concentration, extracts are able to be used in a variety of ways from ingestion, to inhalation and even topical application. Because of this, there are plenty of products and ways to use cannabis extracts:
Dabs: What may be the most straightforward and effective methods to use extracts, “dabs” are simply using the mairjuana extract directly through inhalation. The term “dabs” comes from the fact that a very small amount of extract is equivalent to a larger amount of cannabis flower. Dabs are often vaporized using water pipes with a heated nail commonly referred to as a “rig” or in a vaporizer pen capable of heating up the extract.
Edibles: Extracts are often capable of use in a variety of edible recipes. Using oils, distillates and isolates, recipe ingredients like butter and oil can be used just as they normally would to create any number of recipes that incorporate cannabis extracts.
Vaporizers: Similar to dabs, vaporizer cartridges are wildly popular in the cannabis industry currently. A distillate is used to pre-fill a vaporizer cartridge that can be purchased and is ready for use with one’s own vaporizer device. These are often popular because they are discreet, effective and last a long time for the user.
Tinctures: Distillates and isolates are often used in the form of a sublingual tincture as well. While these are often popular in the CBD industry, tinctures made with specific ratios containing higher THC concentrations are also available.
Topicals: While less common than the other product formulations, some topicals like lotions and creams contain a specific ration as well that may contain a higher quantity of THC and CBD. Though not as much of these cannabinoids are absorbed through the skin, some of them are making it an option for nerve pain, and other dermatological disorders.
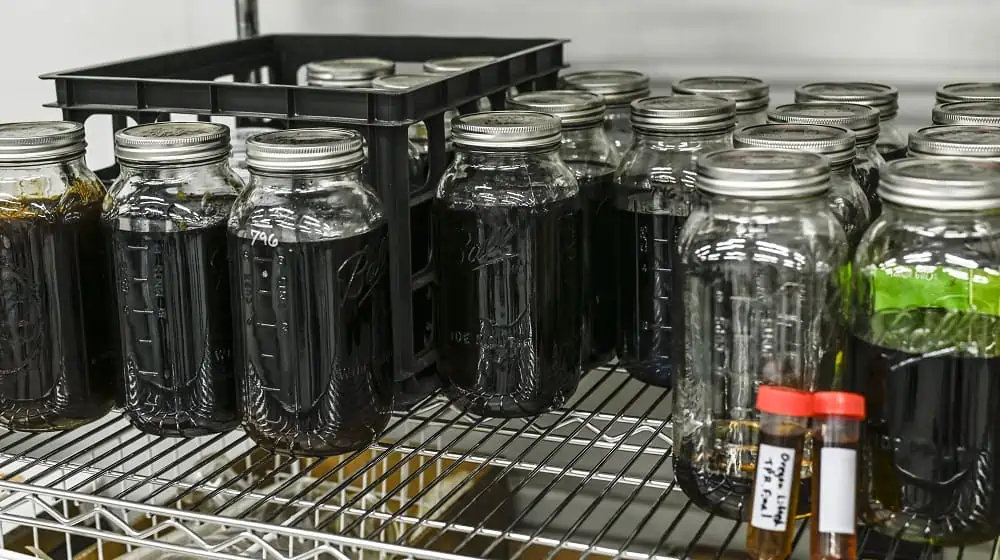

Final Thoughts
It is clear at this point that the cannabis industry is not going anywhere and is only innovating and improving as time moves on. The cannabis extraction industry is a clear indication of this. With so many possible products that come from marijuna extraction, it is critical for producers in the industry to realize the potential of the extraction industry and join in in order to be relevant and profitable.
In order to do this in the most efficient way, choosing the right cannabis extraction method is critical. While there are a number of solvents and methods that can be used, among the very best is found in supercritical CO2 extraction. The reason for this is because CO2 is incredibly efficient, selective, safe and low-cost as an extraction solvent. Therefore, anyone looking to start, or expand their cannabis extraction business would be wise to study the vast benefits of supercritical CO2 extraction for customer health and long-term profitability.
Supercritical CO2 Machine Product Tour
Get access to extraktLAB’s line of supercritical CO2 extractors which are considered the highest in quality, efficiency, and GMP compliance in the hemp and cannabis extraction industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the solvent loss for ethanol extraction?
Hemp and cannabis biomass is an extremely absorbent material. As a consequence, a large amount of solvent volume must be added to the biomass to first solvate the biomass and then fluidize it. For ethanol extraction, approximately one gallon of ethanol is required to extract 1 lb of hemp. Solvent loss comes from the incomplete recovery of that solvent from the hemp.
The following table details the estimated solvent loss from ethanol extraction as a function of volume of hemp processed:
| Lbs processed per day | Daily requirement of
ethanol (gallons) |
Daily Loss of ethanol (gallons) at 90% recovery of ethanol | Max Cost of Solvent Loss per day:
$16-30/gal food grade ethanol $6-8/ gal denatured Calculated at $30/gal |
| 500 | 500-1500 | 50-150 | $1,500-45,000 |
| 1000 | 1000-3000 | 100-300 | $3,000-9,000 |
| 2000 | 2000-6000 | 200-600 | $6000-18,000 |
| 10000 | 10000-30000 | 1000-3000 | $30,000-90,000 |
Another source of solvent loss is incomplete recovery of solvent from the CBD hemp oil.
How many times can I recycle or reuse ethanol from an ethanol extractor?
In guidance published by the FDA in 2010, plans for the reuse of solvents must be accompanied by a Declaration of the maximum number of times the solvent can be reused.
the FDA has recognized that contaminants buildup in the solvent over time as they are recovered and reused
As a consequence, the FDA guidelines recommend that the solvents be brought back to a suitable state before Reuse. A suitable reuse is defined by the original specifications for the solvent that is being used.
In keeping with a risk-based approach to process validation, the key risk to address with solvent reuse is cross-contamination. Cross-contamination could happen when a solvent dissolves a low level contaminant from the biomass being extracted. As the solvent is removed, the contaminant can become magnified and concentrated in either the oil or the solvent during solvent recovery. Cross contamination then occurs when a contaminated solvent is used to extract a non contaminated batch.
Contaminants are typically identified during incoming inspection but may show up later during processing as the oil becomes more refined. Hemp is typically sampled at receiving by quality assurance and a series of tests are conducted on the Hemp biomass in order to determine if the incoming material is contaminated with pesticides, solvents, heavy metals or if it has significant microbial content. Contaminants that are identified in the quality inspection should be tested for build up in the extraction solvent during validation.
Other sources for contamination include carbon black or activated carbon that is typically used in ethanol extraction to remove chlorophyll from the ethanol. Combustion byproducts that are incorporated into the structure of carbon black can dissolve in the ethanol and contaminate.
According to FDA guidelines, the number of times ethanol solvent can be reused must be validated according to a validation protocol. Once the method and process has been validated, the requirements for testing each reuse batch may not be required depending on the risks identified during the validation study.
As a general rule of thumb, a solvent may be reused successfully 20-50 times. Whatever your company’s current practice is, it is important to define the process, validate the process, establish specifications for reuse, and also set up a testing program to measure for contaminants. In all likelihood, a solvent changeover is probably in your future and it’s cost should not be neglected in your overall operating cost model. It is easy to estimate the cost of solving change over as it is the same as the start-up cost:
| Lbs processed per day | Daily requirement of
ethanol (gallons) |
Cost per gallon:
$16-30/gal food grade $6-8/ gal denatured Calculated at $30/gal |
| 500 | 500-1500 | $15,000-45,000 |
| 1000 | 1000-3000 | $30,000-90,000 |
| 2000 | 2000-6000 | $60,000-180,000 |
| 10000 | 10000-30000 | $300,000-900,000 |
The solvent changeover cost on a 60 day change over cycle can then be estimated on a per year basis according to the following table:
| Lbs processed per day | Change Over Frequency | Cost of Changeover | Max Annual Cost |
| 500 | 60 days | $15,000-45,000 | $270,000 |
| 1000 | 60 days | $30,000-90,000 | $540,000 |
| 2000 | 60 days | $60,000-180,000 | $1,080,000 |
| 10000 | 60 days | $300,000-900,000 | $5,400,000 |
By extension, the solvent testing costs will also be important to address:
| Lbs processed per day | Change Over Frequency | Cost of Testing
(pesticides, solvents), Unknowns testing can be 5-10k USD per unknown. |
Max Annual Cost |
| 500 | 60 days | $200-400 | $2400 |
| 1000 | 60 days | $200-400 | $2400 |
| 2000 | 60 days | $200-400 | $2400 |
| 10000 | 60 days | $200-400 | $2400 |
It is important to insist that unknowns be flagged by your laboratory.
What is supercritical CO2 extraction?
Supercritical CO2 extraction is used in hemp processing in hemp extraction for extracting CBD oil from hemp biomass. You can also be used to extract any Botanical oil from any plant material.
The co2 extraction typically takes place above the supercritical pressure and temperature for CO2. Is 1,070 PSI and 31 degrees Celsius.
Under supercritical conditions, the CO2 behaves much like hexane in terms of its solubility selectivity.
Does ethanol extraction have a greater throughput than CO2 extraction?
Hemp processing equipment can be scaled for 1 to 5 tons of extracted hemp per day. It’s generally not a fair comparison to compare the throughput on an instrument from two different companies. What is fair is to specify the throughput At the tonnage process per day and then look at the operating cost for that process. You can also look at the equipment and Facilities cost to accommodate that level of Production. after you have all of your costs accounted for including the hidden costs, then you can calculate the net present value for each investment.
How much hemp can be processed per day with CO2 extraction?
CO2 extraction facilities have been scaled to do hundreds of tons per day of biomass extractions. These facilities are very safe compared to the equivalent extraction facilities that use Flammable solvents.
In Terms of extraction facilities for processing hemp, we have built facilities that will process 5 tons of hemp biomass per day in a safe, low cost, low energy, small footprint operation.
Does it cost less to process hemp with Co2 compared with Ethanol?
Yes.
In fact the operating cost for CO2 extraction is dramatically less than the operating costs associated with ethanol.
Extraction with Ethanol is a process that is typically run at low temperatures. First the ethanol is cooled to below -20oC before it is introduced to the hemp. Cooling the ethanol reduces the amount of extracted chlorophyll and waxes. If you account for the energy required to chill the ethanol down to those low temperatures and then also evaporate after use, the energy bill for extracting ethanol is approximately 3-6x the cost of extracting with CO2. However, the energy cost is really not the key driver in the overall operating costs.
Ethanol extraction requires a significant amount of ethanol to be used per pound of hemp. In fact, about 1 to 1.5 gallons of ethanol must be used per pound of dry hemp in order to extract. Hemp is a very absorbent biomass material and the ethanol must fully saturate the hemp plant before any extraction can take place. For this reason a large volume of ethanol is needed to extract cbd from hemp.
The key cost driver or ethanol extraction is recovery of that solvent from the biomass. Even though many ethanol extraction equipment companies provide centrifuges and or presses to eliminate the amount of ethanol left over in the biomass, The best equipment will provide only a 90 to 95% recovery of the ethanol. This 5 to 10% loss in ethanol is a huge cost driver for extracting ethanol.
For example, suppose you wanted to process 1000 lb of hemp. You would need 1000 gallons of ethanol to start out at a cost of $16-33 per gallon for food grade ethanol for a total cost of $16,000 to $33,000. If you recovered 90% of the ethanol the ethanol loss would be $1,600 – $3,300 per 1000 lbs. Furthermore if you process 1000 pounds per day, this would be your daily loss.
In contrast, you will lose the equivalent of about $70 per day for CO2 extractions for the exact same process.
Besides energy and solvent usage, there are many other hidden costs related to extraction with ethanol including solvent reuse costs, insurance cost, increased facilities cost, and testing costs.
What is the highest yield you can expect from hemp extraction?
Industrial Hemp extraction typically has a CBD content of 5 to 15% by weight. The THC content of the Industrial Hemp is required by law to be less than 0.3% by weight in the flower that is sold.
Does raw hemp moisture affect yield?
Yes, moisture content will affect weight yield. For example, if 10% of the hemp To be extracted was water, and that water was removed during CO2 extraction, the denominator would be larger in the yield calculation, thereby giving a smaller yield number. By extension, if the same hemp was extracted but had zero water in the hemp, the overall weight percent yield of the extract would be a greater percent of the weight.
One thing to note is that in ethanol extraction, water that is in the hemp will dissolve into the ethanol. If the ethanol is removed from the CBD oil with a falling film evaporator, some of the water will be Co evaporated with the ethanol, thereby increasing the amount of water in the ethanol for each extraction cycle. Some of the water will stay in the extract and is typically removed in a secondary stirred reactor before wiped film evaporator and distillation.
Do you offer training on hemp processing and hemp extraction?
We Have taught hundreds of customers how to extract CBD oils from hemp and THC oils from cannabis. Our training package typically includes installation of the equipment, standard operating procedures, commissioning of the equipment in the facility, and training of operators on the procedures that are provided.
We also offer advanced training and quality management system implementation services for those companies who wish to achieve GMP certification.This training dresses all aspects of the quality management system, laboratory information management, batch record system, and Manufacturing execution.
What kind of employees do you need for hemp processing or hemp extraction?
There are basically four different employees that you need to have in order to run a hemp processing or hemp extraction facility. These are as follows:
- assurance
- Shift manager
- Operators
- Optionally analytical operators.
If your goal is to produce a quality product that complies with GMP requirements, you are going to need to have staff that can help you comply with those requirements.That typically means you need to have a quality assurance manager that is aware of the requirements And can Implement those requirements in your facility.
It is also necessary that you have a shift manager. This is someone who is organized and can schedule operators at each station and track the production output. This person will also ensure that operator training has occurred, ensure that yields are met, and also manage the workforce. They are also responsible for producing products that can form with the quality requirements of the end product.
Operators typically execute on the production plan by following standard operating procedures. They are typically trained on how to use the equipment and how to move materials in and out of the process. It is their job to record the data for the quality management system. The Operators typically will be successful if they are Hands-On and are able to follow instructions. It is also a big Advantage if the operator can conduct basic maintenance on the equipment. This requires someone who is Hands-On and has the physical strength to do simple maintenance tasks. This is important for the proper running in the efficiency of a hemp processing facility.
Last but not least, analytical operators or quality control technicians are important for providing yield and in-process testing to the manufacturing facility. They will work with quality assurance directly to ensure that incoming raw hemp biomass conforms to purchasing specifications and to Quality specifications. Quality control technicians are typically chemists and have a laboratory background.